Therapeutics R&D Advanced cell / gene-based biopharmaceutical development and CDMO

-
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, CMT
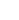
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is a hereditary neuropathy characterized by abnormalities in the motor and sensory functions caused by damage in the myelin sheath that surrounds nerves.
-
Disease Progression in CMT
The onset period of the symptoms differs by individual, and the patients experience gradual atrophy, weakness, and loss of sensations in the foot and hand muscles.
The severity of the symptoms ranges from very mild condition with no difficulties in daily life to needing a wheelchair.
-
The causes of CMT
There have been approximately 70 causative genes implicated in CMT so far. However, in about 50% of the patients, the causative genes have not been identified yet. In order for the nerves to function normally, they need an insulating lipid layer called myelin sheath.
CMT is caused by the damages in myelin sheath.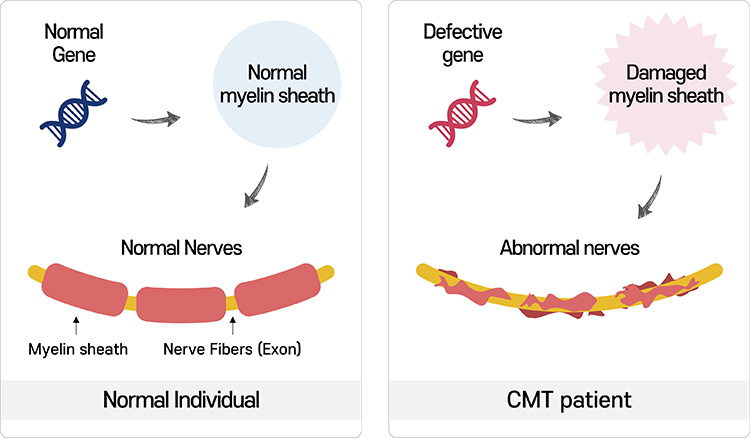
The major symptoms suffered by the CMT patients are as follow.
-
Major clinical symptoms
 Muscle weakness starting from the lower extremities.
Muscle weakness starting from the lower extremities. Lack of sensation such as pain and warmth in hands and feet.
Lack of sensation such as pain and warmth in hands and feet. Wasting of the calf muscle. (stork leg)
Wasting of the calf muscle. (stork leg) Cavus foot (foot with high arch)and hammer toe (toe curled in a Z-shape)
Cavus foot (foot with high arch)and hammer toe (toe curled in a Z-shape)
-
Major biological symptoms

-
Prevalence of DMD
-
Treatments
The currently available treatment options for CMT are as follow. Assistive Devices to prevent foot drop
Assistive Devices to prevent foot drop Physiotherapy or occupational therapy
Physiotherapy or occupational therapy Drugs that slow the disease progression (e.g. ascorbic acid, PTX3003 etc.)
Drugs that slow the disease progression (e.g. ascorbic acid, PTX3003 etc.)
Recently, there have also been several attempts with clinical trials on gene therapy using gene editing.

-
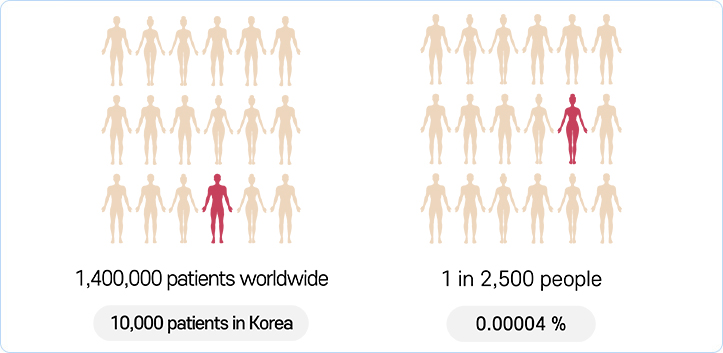
EN001 is a human Wharton's jelly-derived
mesenchymal stem cells (WJ-MSCs)
based cell therapy developed by
ENCell Co., Ltd. for CMT patients.
-
EN001 is a human Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells (WJ-MSCs) based cell therapy.
EN001 is mesenchymal stem cells derived from wharton's jelly (umbilical cord) using proprietary technology developed by
ENCell Co., Ltd.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Mesenchymal stem cell is a type of adult stem cell derived from tissues such as umbilical cord, bone marrow and adipose tissue.
Mesenchymal stem cells are already used as treatments for myocardial infarction, osteoarthritis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis etc.
There are in total 8 types of mesenchymal stem cell based therapies in the market and they have shown high safety profile.
Safety of EN001
The safety of mesenchymal stem cell has been confirmed in over 8,000 cases of clinical trials conducted worldwide, and not a single serious adverse event has been reported so far.
Therapeutic efficacy of EN001 in CMT

Therapeutic efficacy of EN001 was confirmed in a preclinical trial using C3 mouse, a mouse model for CMT.
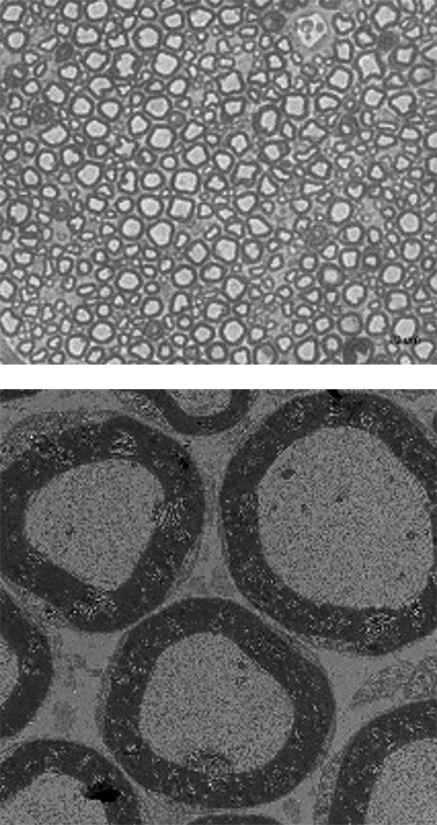
Normal mouse
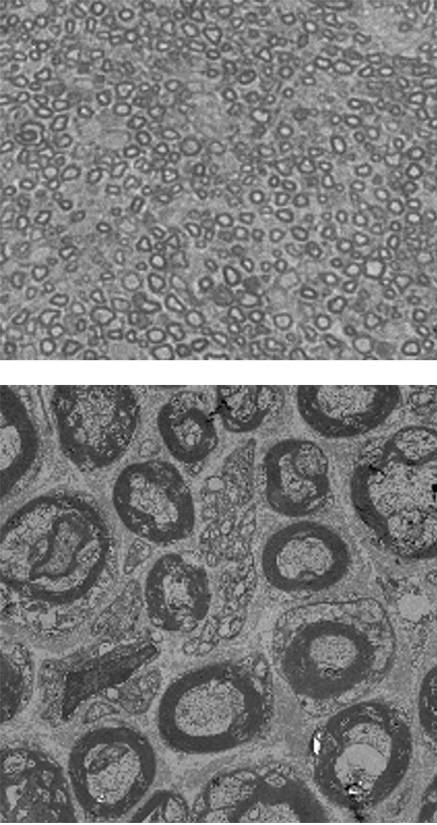
CMT mouse
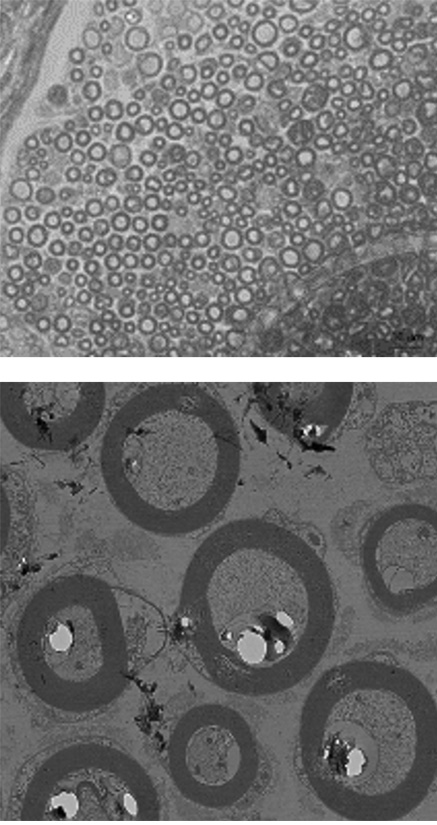
EN001 Administration
The myelin sheath surrounding the nerves are stained in dark grey. It was observed that the myelin sheath is thinner and unstable in CMT mouse compared to the normal mouse.
However, when EN001 was administered to the CMT mouse, thicker and healthier myelin sheath were observed.
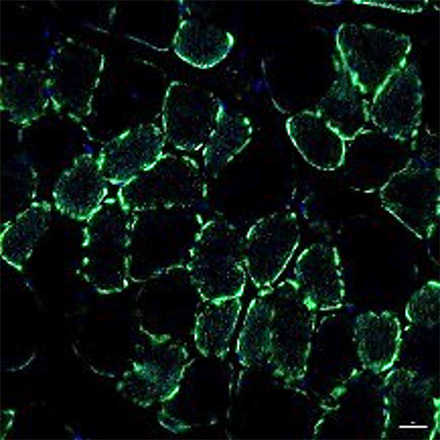
Normal mouse
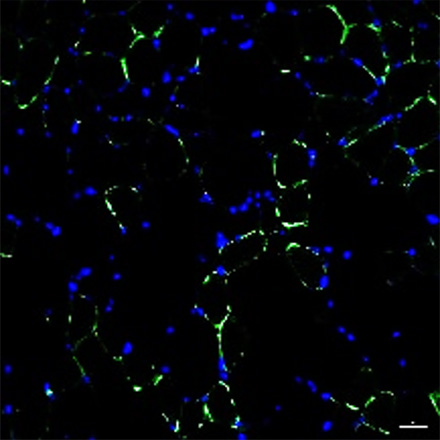
CMT mouse
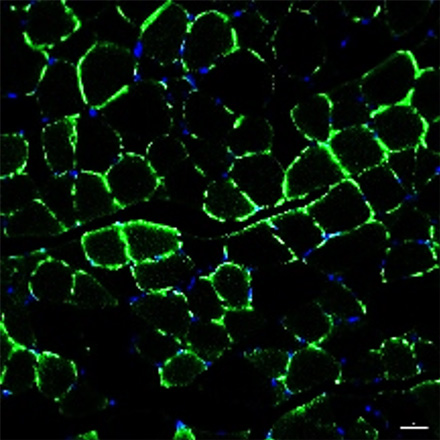
EN001 Administration
Healthy muscle cells are stained in green. It was observed that there are less healthy muscle cells in the CMT mouse compared to the normal mouse.
However, when EN001 was administered to the CMT mouse, an increase in the healthy cells (regeneration of muscle cells) was confirmed.